Multilingual portals
General
Each Intrexx portal can be created in multiple languages.
The language and region are represented by ISO-639 and ISO-3166 codes (e.g. en-us for English (United States of America) or en-gb for English (United Kingdom). These codes are the basis for controlling languages in portals.
Multilingual does not just mean presenting texts in a language-dependent manner, but also presenting number and date values in the respective country. Even colors can be interpreted differently depending on the culture. Graphics with lettering also get a language-dependent aspect. Even the question whether the user reads from left to right or vice versa can play a role.
For multilingual portals, a number of details need to be considered and implemented - regardless of the technology used. You can find the necessary information on this topic here.
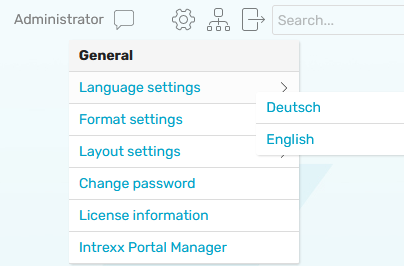
Language switch in the browser
The additional control "Language switch" from the "Design" module is used for switching the language in the browser. The languages, which should be selectable here, must be activated in the Regional settings.
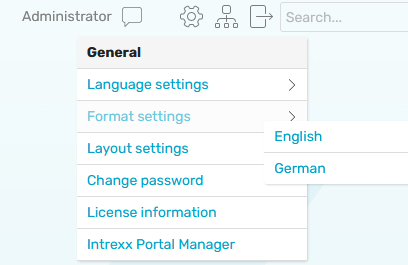
To switch to another format, used to format the date according to the region, for example, the additional control Locale switch from the "Design" module is used. The formats, which should be selectable here, must be activated in the Regional settings.
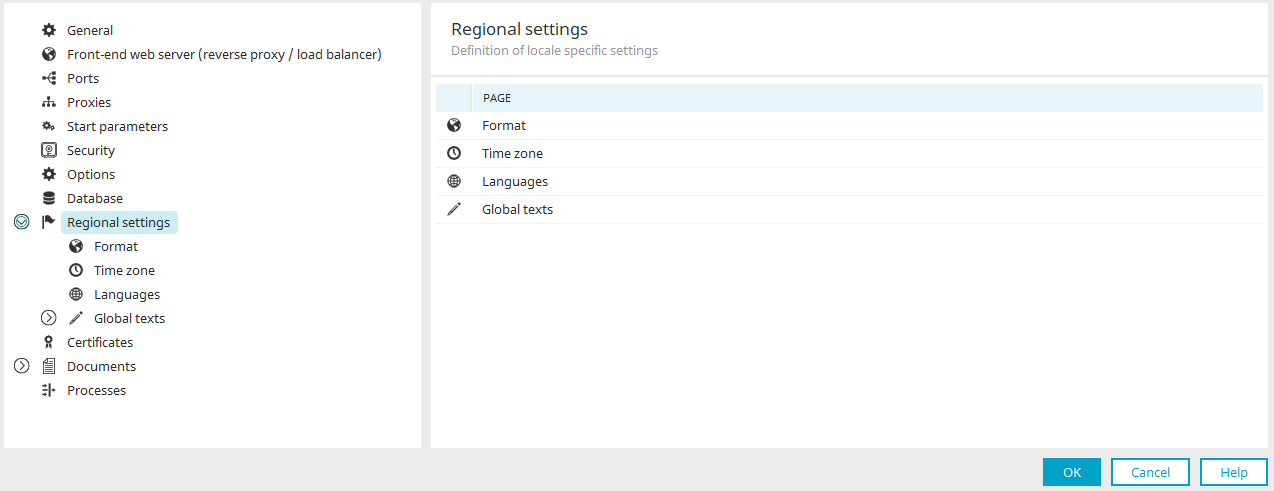
Portal properties - Regional settings
In the portal properties, accessible via the Portal menu, you will find the "Regional settings". The portal can be configured for international use here.
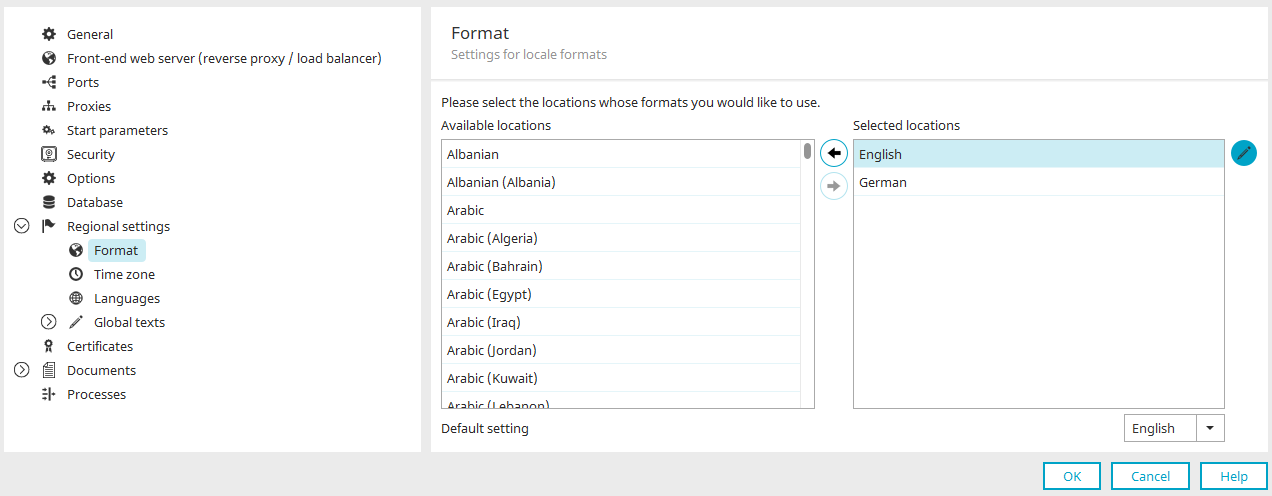
Format
Different formats for displaying date and number values are used across the world. To provide portal users with the option to use formats that correspond with their region, so-called formats can be defined.
Available locations
This list shows all of the formats that can be selected.
Selected locations
This list shows all of the formats that have been activated for this portal.
Select / Deselect formats
Use the ![]()
![]() arrow buttons to move the selected formats to the other list.
arrow buttons to move the selected formats to the other list.
Default setting
Select which language should be used for the default setting in the drop-down list beneath the languages.
![]() Edit formats for the selected location
Edit formats for the selected location
Opens a dialog where the date and number format for the currently selected location can be edited.
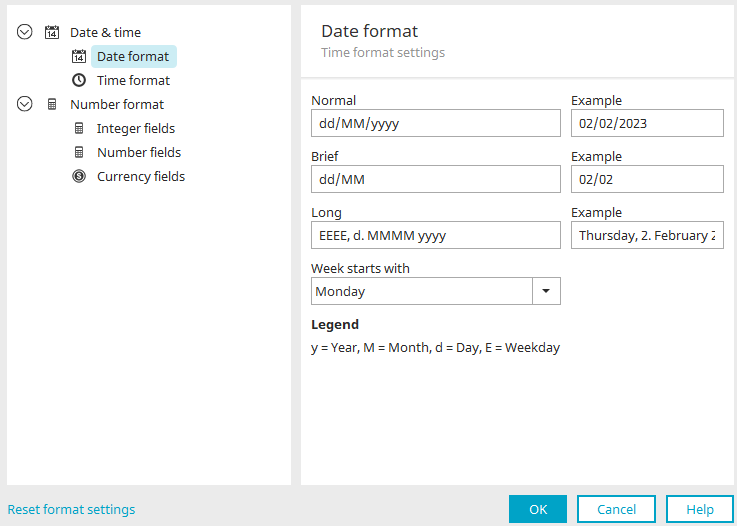
Date format
Normal / Brief / Long
There are three options for displaying the date in the browser: "Normal", "Brief" and "Long". For defining the format, the pattern from the Java SimpleDateFormats can be used.
Example
A preview of the formatted date will be shown in each of the example fields.
Weeks starts with
Set the day on which the week begins here.
Legend
Provides an explanation of the abbreviations used in the "Normal", "Brief" and "Long" fields.
Reset format settings
Resets all format settings back to the default settings for the selected locale.
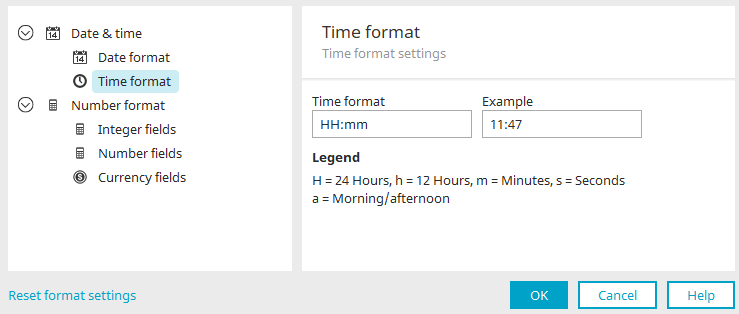
Time format
Time format
For the display of the time in the browser, the format can be defined using the pattern from the Java SimpleDateFormats.
Example
A preview of the formatted time is shown here.
Legend
Provides an explanation of the abbreviations used in the "Time format" field.
Reset format settings
Resets all format settings back to the default settings for the selected locale.
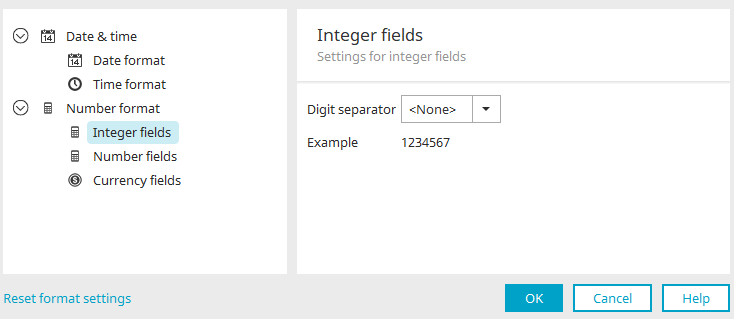
Number format - Integer fields
Thousands separator
Select a character of your choice that should be used to separate 1000s in the browser.
Example
A preview of the formatted integer is shown here.
Reset format settings
Resets all format settings back to the default settings for the selected locale.
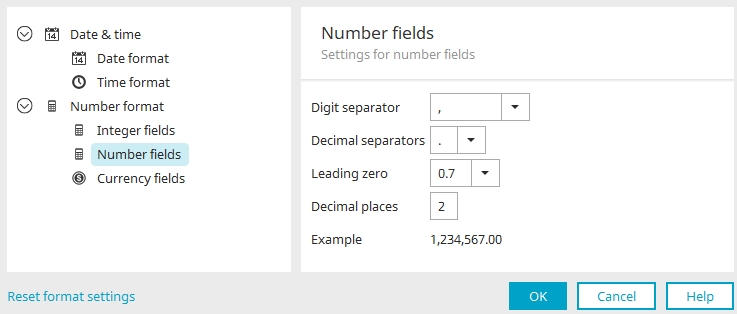
Number format - Number fields
Thousands separator
Select a character of your choice that should be used to separate 1000s in the browser.
Decimal separator
Select a character that should be used as a decimal point in front of the decimal places.
Leading zero
Here, define whether a leading zero should be shown or not.
Decimal places
Define how many decimal places should be shown here.
Example
A preview of the formatted number is shown here.
Reset format settings
Resets all format settings back to the default settings for the selected locale.
Number format - Currency fields
Thousands separator
Select a character of your choice that should be used to separate 1000s in the browser.
Decimal separator
Select a character that should be used as a decimal point in front of the decimal places.
Leading zero
Here, define whether a leading zero should be shown or not.
Decimal places
Define how many decimal places should be shown here.
Example
A preview of the formatted number is shown here.
Reset format settings
Resets all format settings back to the default settings for the selected locale.
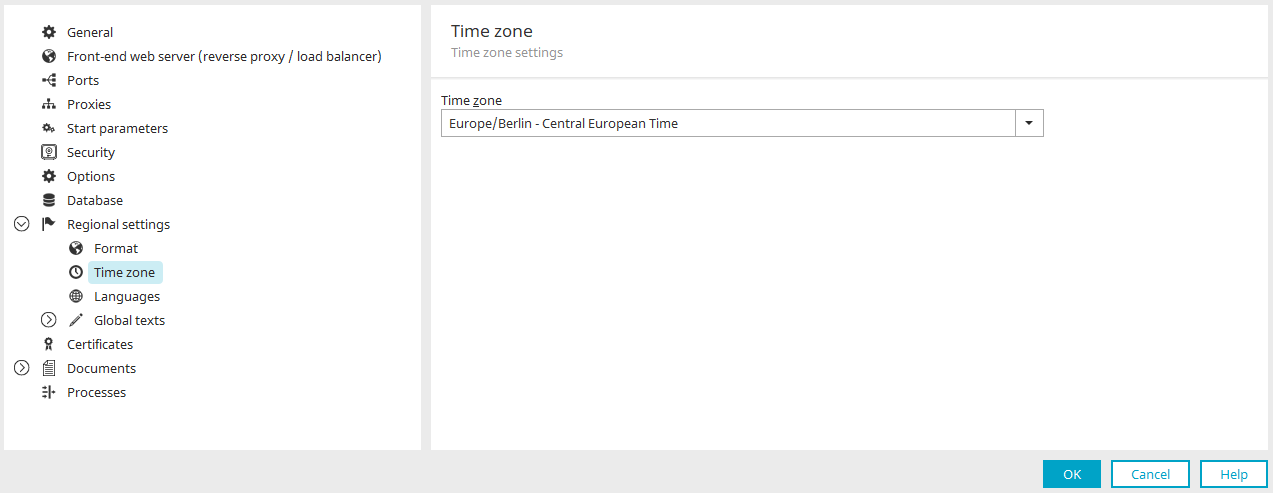
Time zone
A time zone can be assigned to the portal here. Usually, this is the time zone of the server or the company headquarters. If portal users work in different time zones, these time zones can be assigned to a user in the user properties in the Users module. The time zone specified in the portal properties will be used if a custom time zone is not defined for a user.
In Intrexx, every date value is stored in UTC Universal Time Coordinated (GMT Greenwich Mean Time) in the database. When the time is shown in the browser, the difference of the current time zone will be added or taken away from the UTC. The database obtains the time zone setting from the operating system. The time zone of the Intrexx Portal Server and the database should be identical as a general rule. If the database time zone and Intrexx time zone are different, this could result in deviations in the calculation of the local time.
Date values, e.g. date of birth, that should not be changed, should be stored as text information when in doubt and if required, processed with Velocity when it should be displayed (formatting).
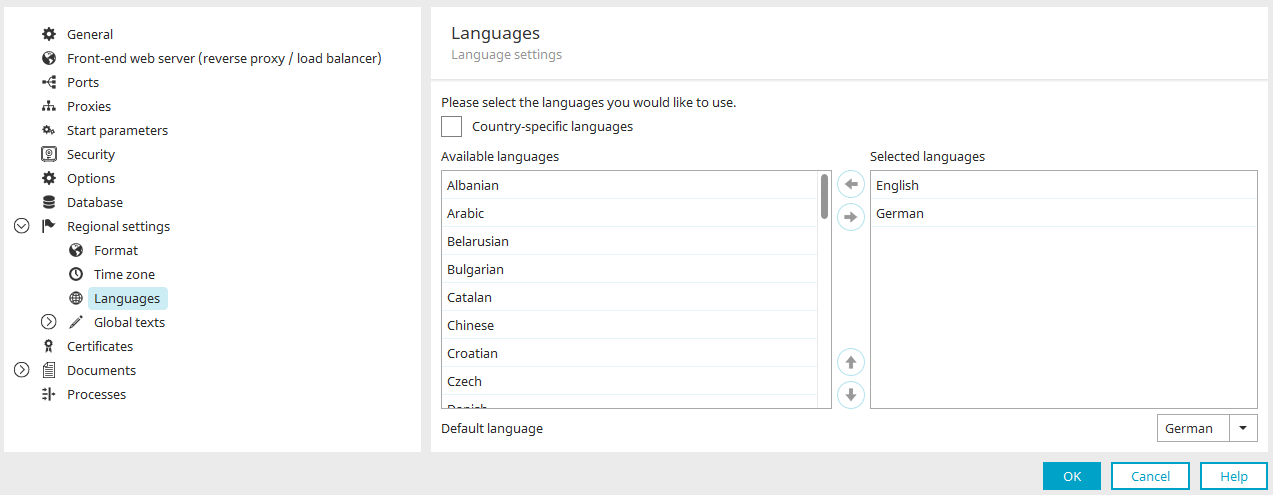
Languages
Any number of languages can be activated for your portal.
Country-specific languages
With this setting, localized languages such as "English (United Kingdom) can be used. When you click on "OK", the internal global language constants will be adjusted and supplemented. Intrexx checks whether the parent language of the localized language is already in the portal, i.e. "English" in this example. If this is not the case, Intrexx checks whether there is another localized version of the language in the portal, such as "English (United States)". If this cannot be found either, the default portal language is used to create the new global language constants.
Available languages
This list shows all of the languages that can be selected.
Selected languages
This list shows all of the languages that have been activated for this portal.
![]()
![]()
Move the currently selected language from one list to the other.
![]()
![]()
Modify the order of the languages, e.g. for the Language switch drop-down list.
Default language
The default language is used if, for example, language data for element titles is missing for the selected language. The default language is entered automatically as the default language for a newly created user to begin with.
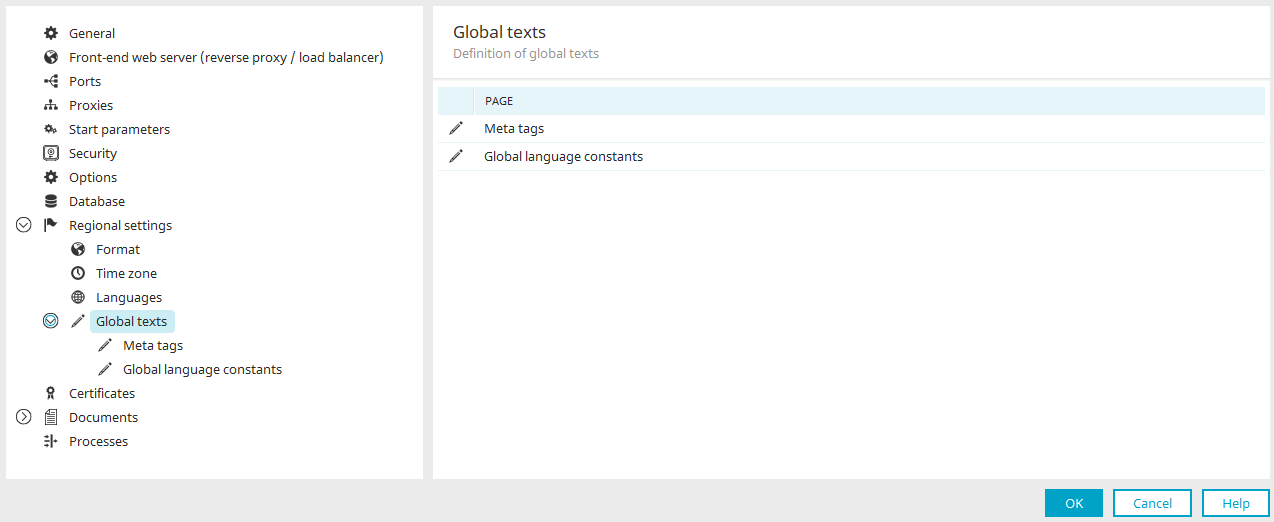
Global texts
In the global texts area, the default texts that appear in the portal can be modified in each of the portal languages.
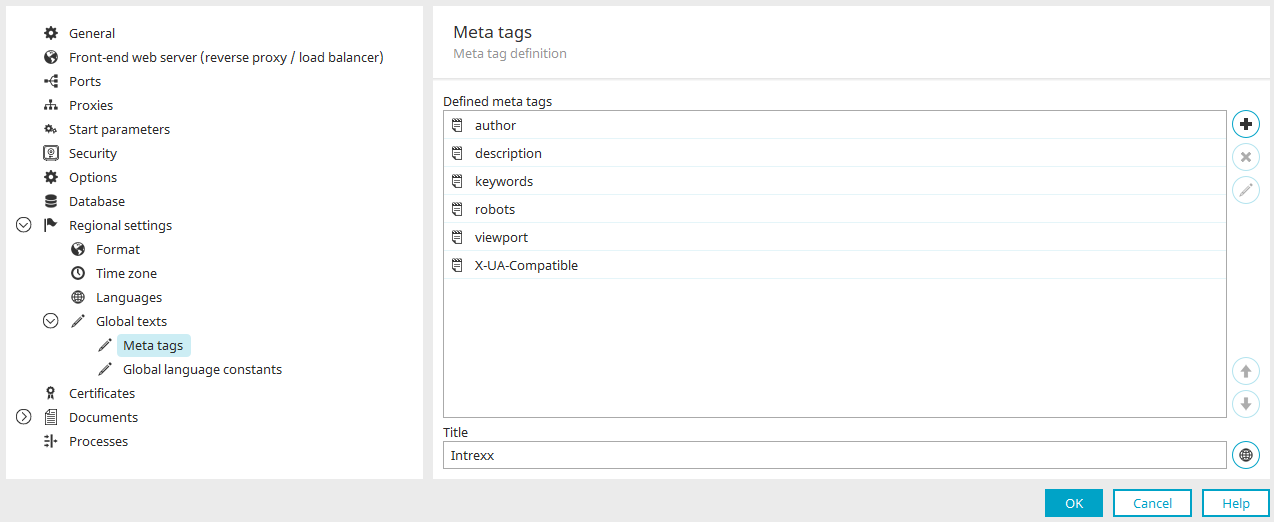
Meta tags
With meta tags, information for web servers, browsers, and automatic search programs on the internet can be provided. Meta tags are HTML tags that describe the contents of an HTML page. Search engines will, with the help of meta tags, create entries in their databases or calculate weightings in a list of hits.
INTREXX Ltd Assumes no liability for errors made while editing meta tags.
Defined meta tags
All of the portal's meta tags are listed here.
![]() Remove meta tag
Remove meta tag
Removes the meta tag currently selected.
![]()
![]() Move up / Move down
Move up / Move down
Modify the order that the meta tags are written to the HTML in.
Title
The title is written in the "<title>" tag of each portal page.
![]() Multilingualism
Multilingualism
Opens a dialog where the title can be edited in the portal languages. The multilingual title cannot be connected to global language constants in meta tags.
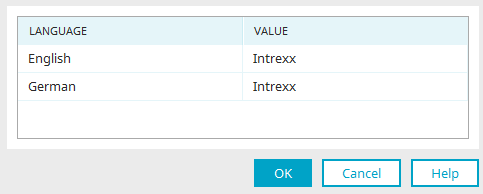
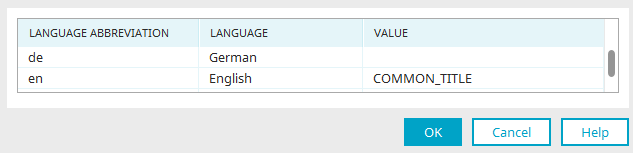
"Language" column
The activated portal languages are shown here.
"Value" column
Enter the corresponding term in each of the languages.
![]() Add meta tag /
Add meta tag / ![]() Edit meta tag
Edit meta tag
Opens a dialog where a new meta tag can be created and existing meta tags can be edited.
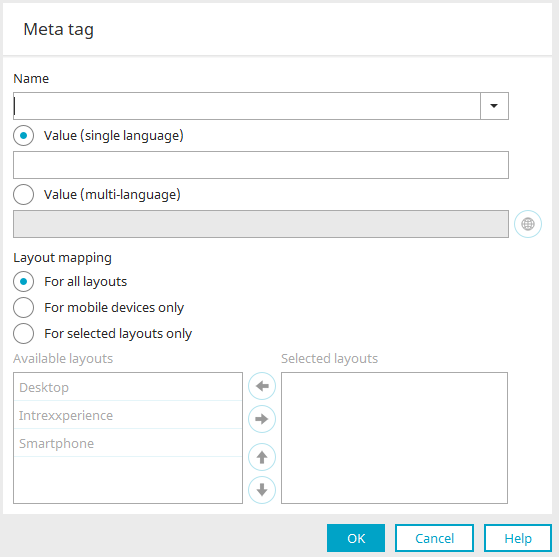
Name
You can select the most common meta tags here. You can also define custom meta tags Simply by entering the name of your meta tag without selecting an existing meta tag.
Value (single language)
Values for single language meta tags, such as "Robots=nofollow", can be entered here.
Value (multi-language)
With this option, values can be entered in each of the portal languages.
![]() Multilingualism
Multilingualism
Opens a dialog where the title can be edited in the portal languages. The multilingual title cannot be connected to global language constants in meta tags. Click "OK" to save the changes and close the dialog.
Layout mapping
For all layouts
The meta tag will be generated in all portal layouts with this option.
For mobile devices only
The meta tag will only be generated in pages which have been transformed for mobile devices.
For selected layouts only
The meta tag can be released for individual layouts here.
Available layouts
All layouts that can be selected are listed here.
Selected layouts
All layouts are listed here where the meta tag is entered.
![]()
![]()
Move the currently selected layout from one list to the other.
![]()
![]()
Modify the order of the layouts in the list.
Meanings of meta tags
-
Description
The description may not exceed 200 characters. In the "Description" tag you will enter information about the company, product, people, or page contents.
-
Keywords
Keywords consist of individual words or expressions and should be separated with commas. With these keywords, the contents of the page will be summarized and output in variations. Select some appropriate formulations that a user would search for on the internet in order to find a page of your portal.
-
Robots (Instructions for search engines)
Here you will define how the page will be handled by robots, which index pages for search engines.
-
noindex
Forbids the page from being indexed
-
index
Request for the page to be indexed
-
follow
Index page and follow links to additional pages
-
nofollow
Do not index page, do not follow links
There are a large number of additional meta types of information that can be entered. For more information on the topic, please search for literature on the topic of web design or the Internet.
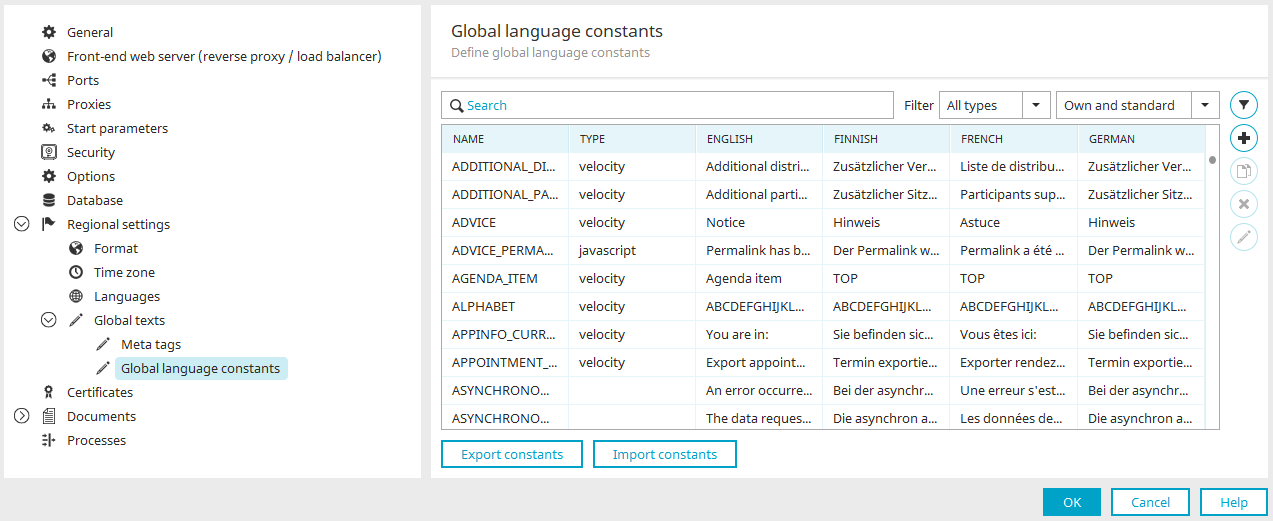
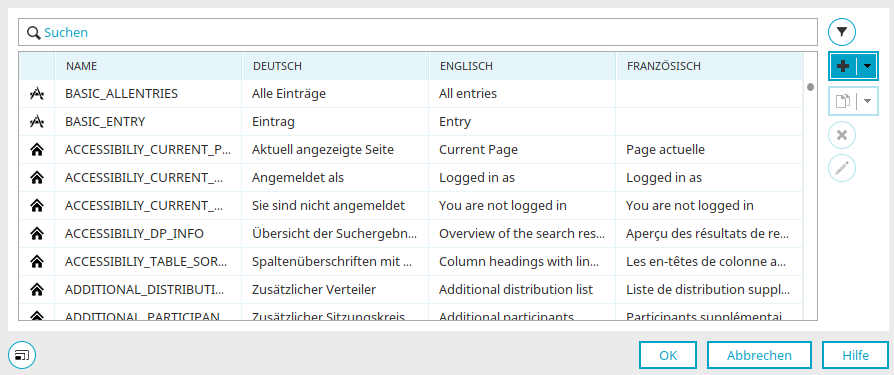
Global language constants
Every text element used by default in Intrexx is defined in the global language constants. Furthermore, you will find specific language constants for Intrexx Share. This helps you to administrate texts that appear in the portal often and in many applications centrally.
Search
Enter a search term here. Simply enter the desired term to do so.
Filters
Type
You can filter the list by constants that are used in JavaScript or Velocity.
Own / Standard
With this filter, you can decide whether your own constants, Intrexx standard constants or both should be shown.
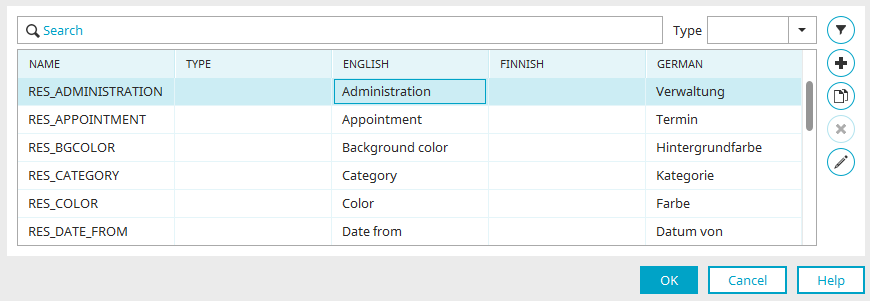
Name column
Displays the name of the language constant.
Type column
The use of the constant is shown here.
Language column
In the following columns, the texts will be shown in the respective portal languages.
![]() Filter languages
Filter languages
Click here if you want to show/hide a language column, e.g. "English", in the list.
![]() Create a copy of the language constant
Create a copy of the language constant
Creates a copy of the constant currently selected.
![]() Delete
Delete
Deletes the currently selected constant created by you. Intrexx standard constants cannot be deleted.
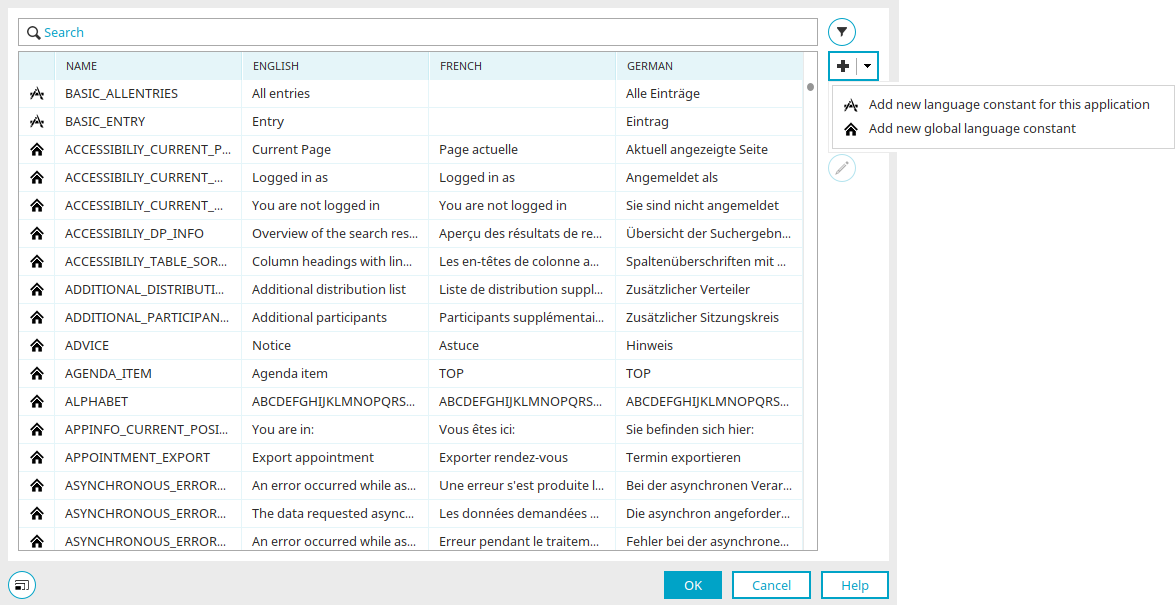
 Add new language constant /
Add new language constant /  Edit language constant
Edit language constant
Opens a dialog where a new language constant can be defined or an existing language constant marked in the list can be edited.
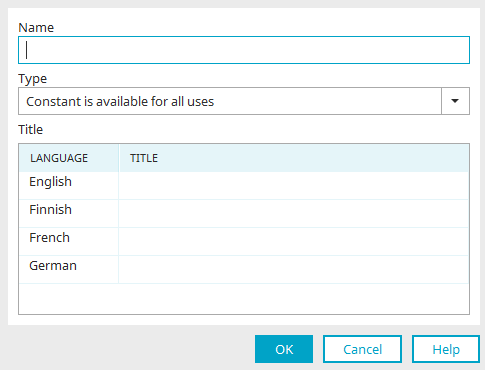
Name
Provide the language constant with a name here. This name will be used later to address the constant in each scope. The name has to be unique. Only use capital letters and avoid using special characters and spaces. The name must start with a letter, followed by letters, numbers or _. Specifying a namespace is recommended to isolate your own constants from the Intrexx standard constants. This can be namespace referring to projects or customers.
Type
Here, you can specify the scope of a language constant:
Constant is only available in JavaScript
The constant cannot be used as a title in applications or in Velocity. Use as few of these language constants as possible because JavaScript always needs to be transferred. Only use language constants in JavaScript for messages in custom check routines (alert(), prompt(), confirm() or Intrexx-Notifier) or for a dynamic output in view text fields. The portal language currently defined is always used in JavaScript. If the first key is not found, the fallback parameter will be searched for next, provided the fallback parameter has been defined. If the fallback parameter also does not deliver a result, "undefined" will be returned.
// Read application constant
ix.text.i18n.getByApp(p_strAppGuid, p_strKey, p_strKeyFallback);
// Read portal constant
ix.text.i18n.get(p_strKey, p_strKeyFallback);
Constant is evaluated as a Velocity expression
The constant is available in Velocity and the Groovy context but not in JavaScript. Constants available for all uses can also be used in Groovy. Only use constants in Velocity for labeling pages. This is the most common application area and should therefore be preferred. This also applies when they are used in Groovy. The language key is entered as the ISO language code (de, en etc.). When accessing application constants, the application's GUID must be specified as a parameter.
## Read portal constant
##(Portal language is used as a criterion)
$I18N.get(p_strKey)
## Read portal constant with default language
$I18N.getByLang(p_strLang, p_strKey)
## Read application constant
## (Application GUID and constant as parameter)
$I18N.getByApp(p_strAppGuid, p_strKey)
## Read application constant with default language
$I18N.getByAppByLang(p_strAppGuid, p_strLang, p_strKey)
## Example
$I18N.getByAppByLang('3E4..2AF', 'de', 'myKey')
Constant is available for all uses
Avoid this setting as much as possible. This type should only be selected if the language constant appears in both of the cases named above. Global constants can be used in Velocity as follows:
$I18N.get("NAME")
Application constants can be used as follows:
$I18N.getByApp(" APPGUID", " NAME")
In Groovy, multilingual text constants can be used to generate log entries or constructions, that, for example, are written back to data fields. The constants can also be implemented for the purpose of labeling when generating data exports via Groovy (e.g. XML files). The object "g_i18n" is available for this purpose, it is initialized with the context language. If the context is missing, the default portal language is used as the fallback.
// Read application constant
def app = g_i18n.application("APPLIKATIONS_GUID")
def appConst = app["APPLIKATION_LANGUAGE_CONSTANT"]
// Read application constant with default language
def appde = app.language("ISO_LANGUAGE_CODE")
// Read portal constant
def portalConst = g_i18n["PORTAL_LANGUAGE_CONSTANT"]
// Read portal constant with default language
def portalde = g_i18n.language("ISO_LANGUAGE_CODE")
def portalConst = portalde["PORTAL_LANGUAGE_CONSTANT"]
// Example: Read application constants explicitly in English
def app = g_i18n.application("3F2…E1A")
def appen = app.language("en")
def text1 = appen["CUSTOMER"]
// Example: Read application constant
def app = g_i18n.application("3F2…E1A")
def text2 = app["CUSTOMER"]
// Example: Reading portal constants explicitly in German
def portalde = g_i18n.language("de")
def text3 = portalde["CAL_WEEK"]
// Example: Read out portal constants
def text4 = g_i18n["CAL_WEEK"]
Title
You can give the language constant a title for each of your different portal languages.
"Language" column
The portal languages are shown here.
"Title" column
The title corresponds to the value that the constant has - it will be displayed when the constant is used in the selected area. Enter the value of your choice here.
Naming rules for language constants
Name your language constants meaningfully so that their use is clear. Using different prefixes can make it easier to differentiate between the names.
|
Prefix |
Used for |
|
COM_ |
General constants used in different place, e.g. for labelling elements on the page or for the page title |
|
ACTION_ |
Label for buttons |
|
TABLE_ |
Texts in tables such as for a notification if data records are available (TABLE_NODATA_) or a table title (TABLE_TITLE_) |
|
OPT_ |
Texts for labels and specifications in the system data group |
|
MSG_ |
Texts in messages via JavaScript |
|
MSG_WARN_ |
Texts in warning messages via JavaScript |
|
MSG_ERROR_ |
Texts in error messages via JavaScript |
|
CONFIRM_ |
Texts for describing notifications in confirm requests |
The "MSG_ constants" are an exception because messages can contain a title and text (Notifier). These can be distinguished by using a suffix at the end of the constant name:
|
Suffix |
Used for |
|
_TITLE |
The message title |
|
_TEXT |
The message text |
If language constants are used for list entries, all specifications for this element should be grouped together language constant list. Use a property after the prefix to group them together - such as the term "ACCESSTYPE". Each of the options "_ROLE, _GROUP" and "_USER" is then added afterwards accordingly.
COM_ACCESSTYPE_ROLE
COM_ACCESSTYPE_GROUP
COM_ACCESSTYPE_USER
There are no hard and fast rules for naming language constants because how the constant names are defined depends on the complexity of the application. The naming examples stated above should only serve as a possible approach.
Portal Manager language settings
You can access this dialog via the "Extras" menu / Options.
Language of the Portal Manager
The language of the Portal Manager can be defined here. The new setting will take effect when you restart the Portal Manager.
Display language of multilingual titles
The language multilingual titles are displayed here can be selected.
Language adjustment
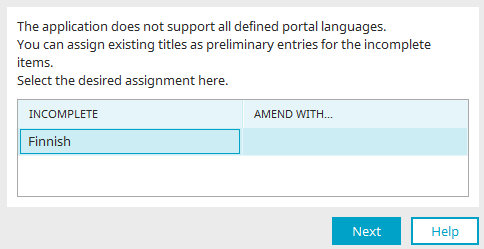
When opening an application, process or layout, a check is performed as to whether every element has been provided with a title in each of the portal languages. If you have, for example, activated an additional portal language, titles will remain blank to begin with. Upon opening, a dialog will be displayed which allows you to transfer the titles from an existing portal language to the empty titles of the newly activated portal language.
The setting to activate a check for missing titles can be activated in the Extras menu / Options menu with the setting "Check for missing titles". This must be done for each module.
Find and translate element titles
In the "Applications", "Design" and "Processes" modules, you can search for items that do not yet have a title in one of the portal languages. Click here for more information.
Exporting and importing texts and language constants
All the information on importing and exporting titles and names of application or process elements can be found here.
Information on importing and exporting global language constants can be found here.
Multilingual titles
Whenever you find the ![]() globe symbol for multilingualism in the Intrexx Portal Manager, you have the option of adding titles, descriptions or similar. multilingual.
globe symbol for multilingualism in the Intrexx Portal Manager, you have the option of adding titles, descriptions or similar. multilingual.
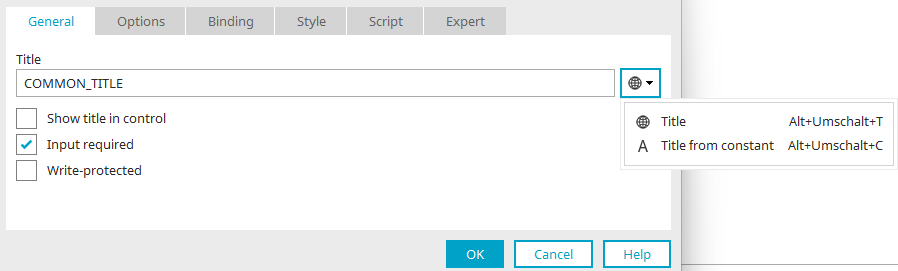
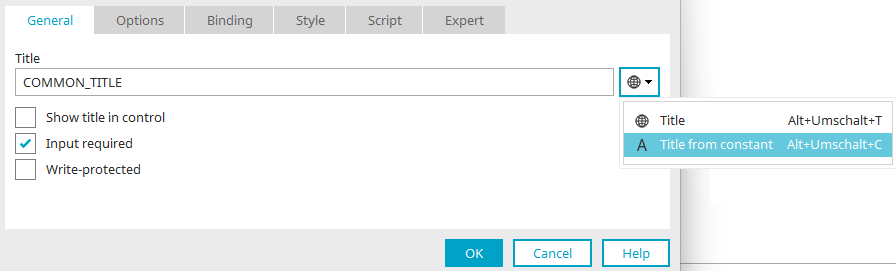
In applications, you will find a button to the right of the title field in the properties dialog of elements. Clicking on the small arrow to the right of this button opens a menu where you can select whether a static title or a title from a constant should be used for the element.
If you select ![]() "Title" here, the button will then display the
"Title" here, the button will then display the ![]() globe icon to the left of the small arrow.
globe icon to the left of the small arrow.
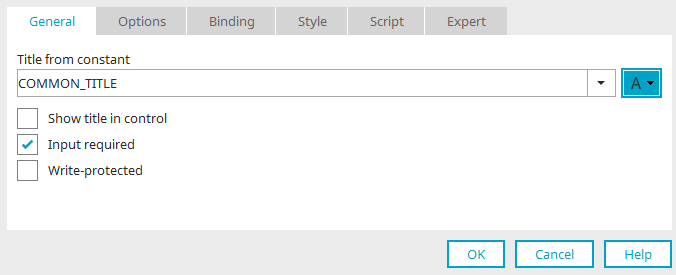
If you select "Title from constant", you will find an "A" on the button afterwards.
Static titles
Click on the ![]() globe icon to open a dialog where a static title can be entered in the configured portal languages.
globe icon to open a dialog where a static title can be entered in the configured portal languages.
The browser will then use the text entered here depending on the language setting in the portal properties. This also applies when the user switches the language.
Title from constant
Constants can be used for element titles in applications instead of static text. In the browser, the text entered for the constants is then used depending on the language setting in the portal properties. This also applies when the user switches the language. Information on how to create constants, edit them and define the multilingual text is available here:
If you have selected "Title from constant" in the properties dialog of elements, the drop-down list for the title will then work like a search.
Simply enter the name of the constant you are looking for and select the constant from the selection list.
Clicking on the "A" in the button to the right of the title drop-down list opens the "Global language constants" dialog where you can also search for constants and edit them directly.
Language switch in modules
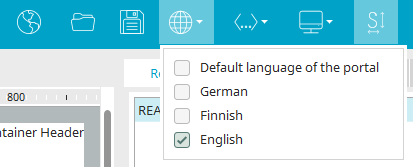
You can switch the language in which the element titles in each of the modules in the Portal Manager are displayed using the ![]() globe symbol in the tool bar.
globe symbol in the tool bar.
Portal menu
For applications, which are integrated into the menu structure, you can define that the application title should be used as the menu item. If the title is already defined in multiple languages, the values for each of the portal languages will be used. If the Use title of application setting is disabled, you need to define the title for the menu item in each of the portal languages. Multilingual titles can also be defined for all other objects such as menu folders, links or separators.
Click here for more information about the menu structure.
Layout
Because each portal layout is an assembly of various containers that, especially for barrier-free concepts, should be understood by screen readers, the containers also need to be provided with multilingual titles. Custom language constants cannot be used in the layout. Each of the elements in the layout uses correspondingly defined global language constants.
User settings
In the Users module, region-specific settings can be defined in the user properties.
The settings defined here for time zone, language, format and layout overrule the settings made in the Regional settings of the portal.
Applications
Language constants in applications In the Applications module, using language constants is not only a good idea for multilingual applications but all applications can benefit from the use of the constants. Because the same text appears in multiple locations, these can be modified much more easily via a central constant. INTREXX Ltd Therefore recommends developing applications from scratch, based on application constants.
Language constants in applications
Constants can also be defined directly in applications, which are then only valid within the application, unlike the global language constants. Constants for applications can be added, edited and deleted via the Application menu / Manage language constants. All information about the settings in the "Mange language constants" dialog is available here.
From Intrexx version 12.0.0
Language constants that are only valid within the application as well as global language constants can be defined in applications.
The corresponding dialog can be found in the properties of application elements. General information on this can be found in the section "Multilingual titles".
If you want to create global language constants, you need the "Manage global language constants" portal permission.
In the "Manage language constants" dialog, click on the small arrow button next to the ![]() "New language constant" button to display a menu that allows you to decide whether the new constant should be valid application-wide or globally. The constant can then be created via the following dialog.
"New language constant" button to display a menu that allows you to decide whether the new constant should be valid application-wide or globally. The constant can then be created via the following dialog.
Constants for applications can be added, edited and deleted via the Application menu / Manage language constants.
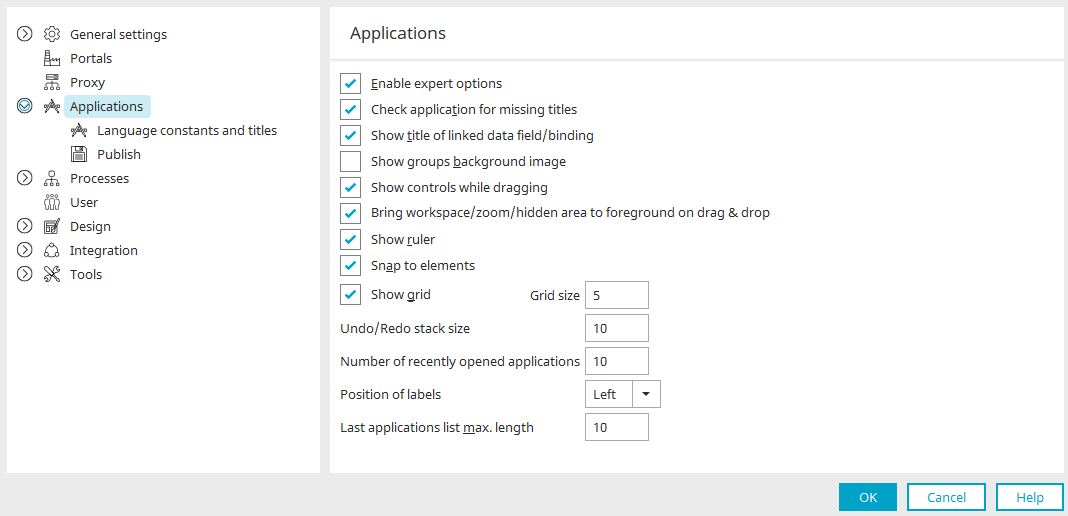
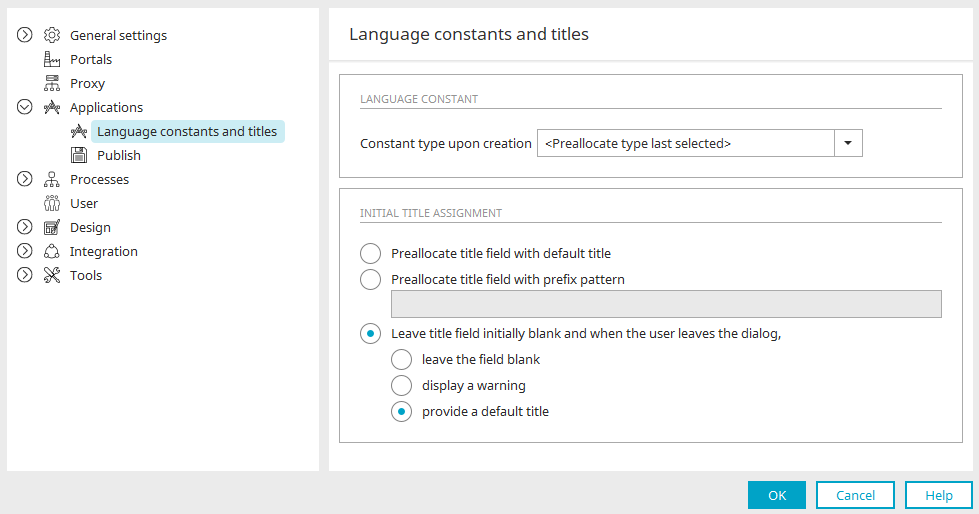
Options - Language constants
The optional settings for language constants and titles are accessed from the main menu "Tools / Options / Applications / Language constants and titles".
Constant type upon creation
Here, you can define the constant type that should initially be assigned to new constants.
Initial title assignment
You can define which type of title elements will be given when they are created in the Application Designer.
Preallocate title field with default title
The title will be taken from the language constant "DEFAULT_CTRL_<Control type>". In the browser, the title will be shown in the current portal language. The title is also applied to data fields and data groups with this setting.
Preallocate title field with prefix pattern
When creating elements, automatically sets the title from constant option and enters the pattern defined here. This preset can also be supplemented by the constant name.
Leave title field initially blank and when the user leaves the dialog,
-
leave the field blank
The title field is left blank when the user closes the dialog.
-
display a warning
A corresponding notification will be displayed, if the title field is left blank when the dialog is closed.
-
provide a default title
The title will be taken from the language constant "DEFAULT_CTRL_<Control type>" if the title field is left blank when the dialog is closed.
Multilingual element titles
You can find out how to provide elements with multilingual titles here.
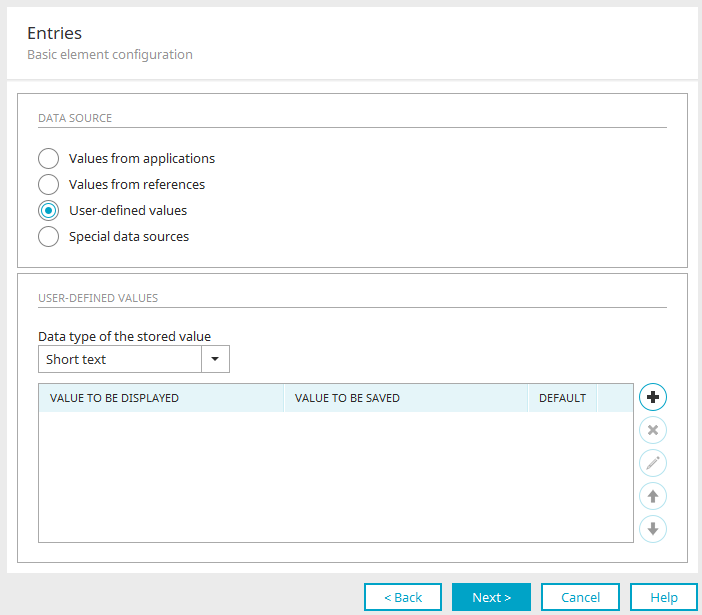
Multilingual list entries
For the elements
you can select User-defined values as the source for the list in the element.
Clicking on ![]() "Edit" opens the dialog for editing the list entries.
"Edit" opens the dialog for editing the list entries.
Constants can also be used here instead of static values. Click on the arrow to the right of the ![]() globe icon. Click here for information on how to select a constant. The displayed value from the constant and the saved value must be identical in this case.
globe icon. Click here for information on how to select a constant. The displayed value from the constant and the saved value must be identical in this case.
Multilingual data records
You can discover how to enter data records in different languages and then display them correctly based on the respective portal language setting in the Tips & Tricks article "Multilingual data records".
Multilingual data with doubled primary key
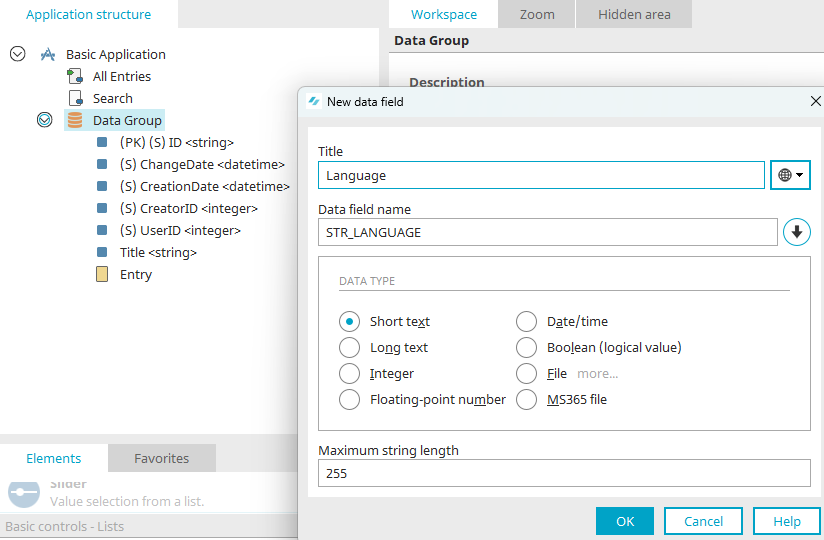
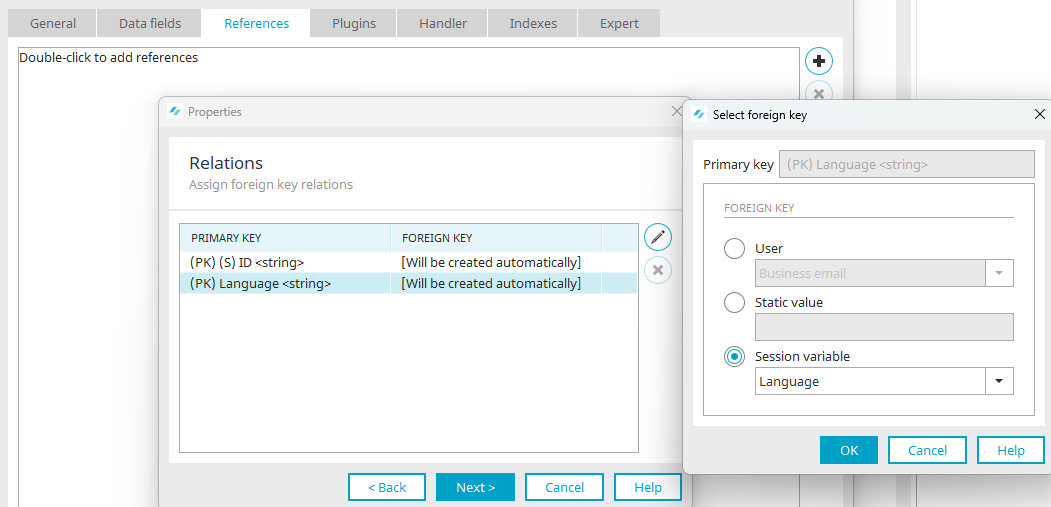
In order to make data available in multiple languages, these can be saved in a data group using the principle of a doubled primary key. This is made up of a key and an ISO language code. For control tables, e.g. for statuses, the key should be a descriptive string. For all other data, it should be a GUID.
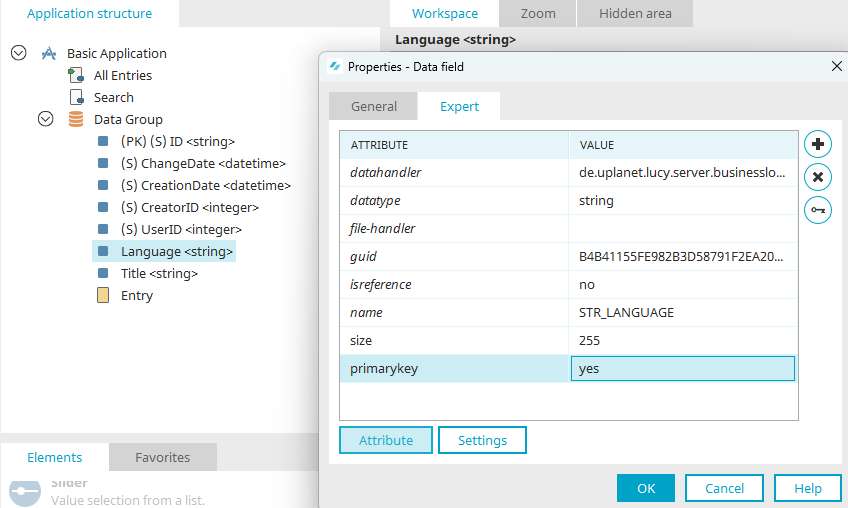
For the second primary key, a new data field titled "Language" is created before publishing the application.
On the "Expert" tab, the expert attribute "primarykey" is set to yes.
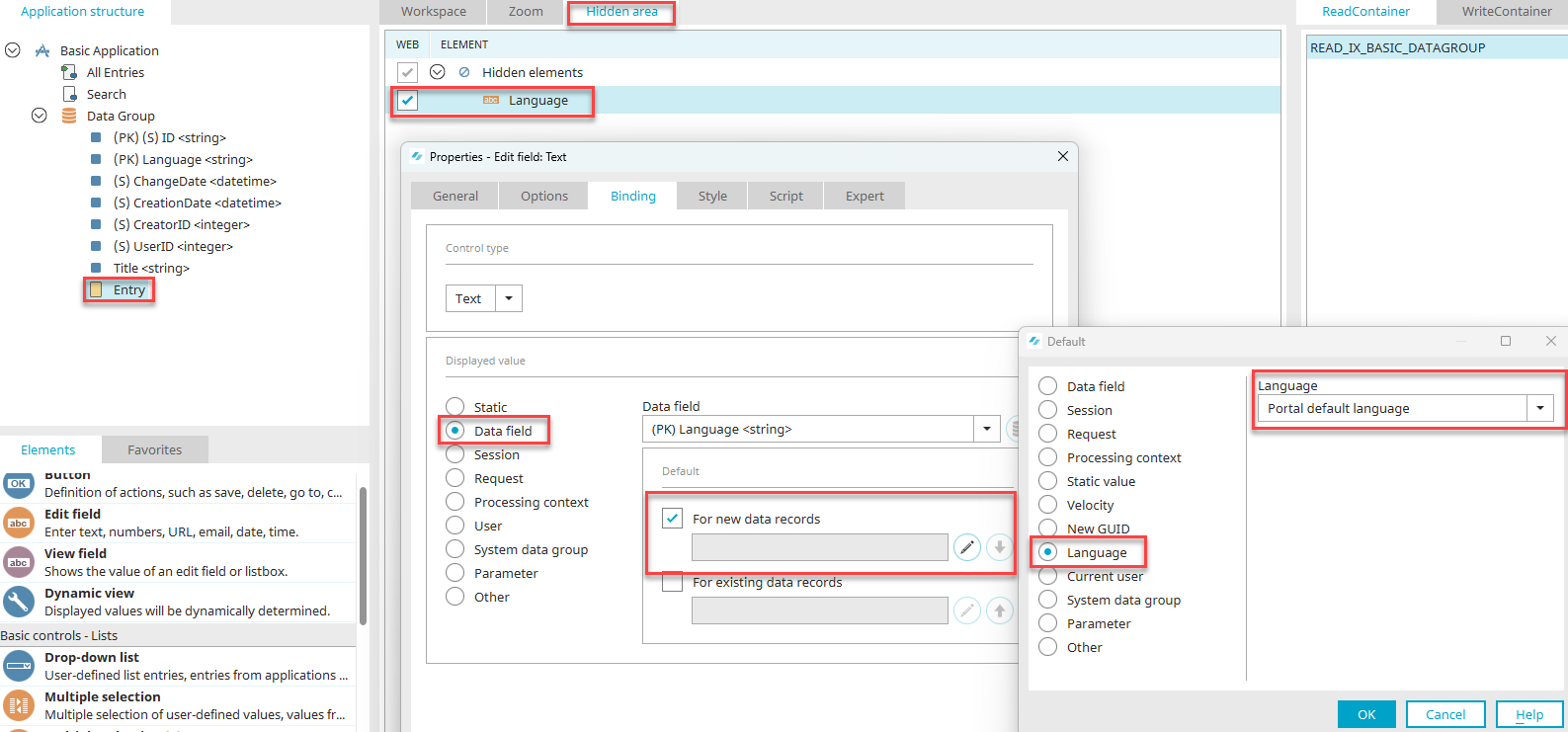
When data records are entered, both primary keys need to be populated with values so that errors do not occur when the data is processed. To do this, the language data field can be connected to an edit field in the hidden area. The input field is preallocated with the current portal language via its binding.
A common scenario for this is using multilingual master data, such as statuses, categories, in moving data records via a reference. If a reference to a data group with two primary keys is created, the session variable "Language" must be assigned for the primary key. The other primary key will be left with the setting "Will be created automatically".
Using the reference, Intrexx will now always provide the corresponding language text in the browser.
Multilingual emails
Email to one recipient
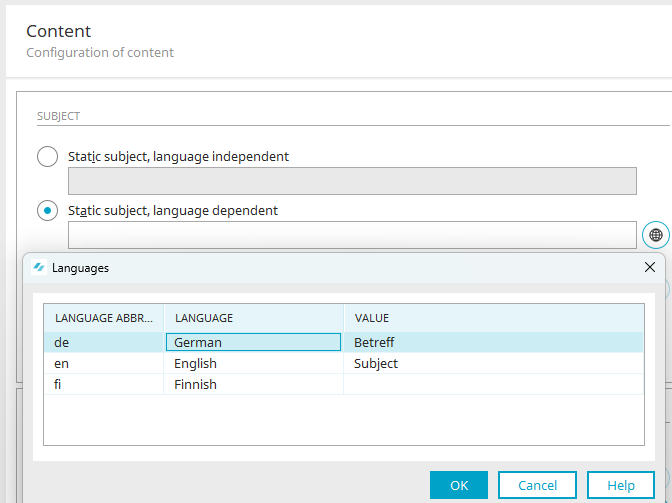
If a user sends an email, their language setting can be identified in a process. The process can use the identified language in an email sent with an Email action.
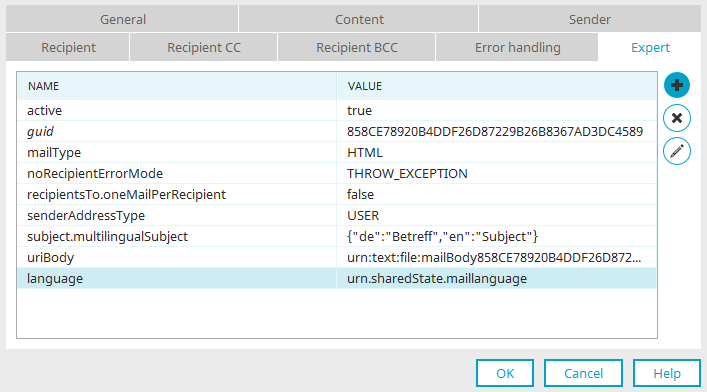
The subject can be defined by translating the language-dependent subject accordingly. In the properties dialog of the email action, the parameter "language" can be added on the Expert tab.
// Language of the current user
def l_strLanguage = Locale.forLanguageTag(g_language).getDisplayLanguage(new Locale(g_language))
// Language of any user
// (via its GUID and the user object)
def l_objUser = g_om.getUser(l_strUserGuid)
def l_strLanguage = objUser.getDefaultLanguage()
// Putting language into the processing context
g_sharedState.maillanguage = strLanguage
In the properties dialog of the email action, the parameter "language" can be added on the "Expert" tab and the language determined from the processing context can be transferred as a value with "urn.sharedState.maillanguage".
The subject can also be defined using a language constant. With the corresponding Groovy method, the language constant's content is read based on the language identified in the previous step.
// Determine subject from language constant and place in processing context
g_sharedState.subject = g_i18n.application("APP_GUID").language(l_strLanguage)["MYMAILSUBJECT"]
The value from the processing context is then entered in the static, language-independent subject of the email action with "urn.sharedState.subject".
If the email is sent via CC and BCC to one recipient with different languages in each case, this method cannot be used. This would require separate handling with an individual email action in each case in the process chain. The message text could also be identified in a preceding Groovy action and then written to the processing context. The processing context can then be read in Velocity and from that, the email body can be generated.
Email to distribution list
There are two approaches to sending emails to a distribution list if these should be sent multilingually:
-
An email action is created for each language where the recipients are selected based on their defined language.
-
The email is generated with Groovy script while taking the language of each user into account. However, the message body needs to be constructed manually in this case.
A possible construction is shown below. In this case, however, only user objects can be recipients via the distribution list.
import de.uplanet.lucy.util.TextUtil
import de.uplanet.lucy.server.mail.GroovyMailBuilder
import de.uplanet.lucy.server.mail.MailUtil
import de.uplanet.lucy.server.portalserver.PortalServerPath
import de.uplanet.lucy.server.composer.UrlBuilder
// Contents of a distribution list (GUIDs of recipients)
def l_strRecipients = g_record["640...DAC"].value
def l_aReceipients = TextUtil.stringToList(strRecipients)
aReceipients.each {
def strEmail = g_dbQuery.executeAndGetScalarStringValue(conn, "SELECT
STRMAILBIZ FROM VBLUSER WHERE STRGUID = ?", null) {
setString(1, it)
}
if(strEmail != null && strEmail != "")
{
def mail = new GroovyMailBuilder().composeMail {
headers = [
"X-IX-Share": "intrexx-share-notification",
]
from = MailUtil.getDefaultSenderAddress()
to = strEmail
subject = l_mailHelper.getMailTitle()
contentType = "text/html; charset=UTF-8"
body << """<html> … </html>"""
}
mail.drop()
}
}
Language switches
To a large extent, you can avoid using language switches in programming codes with language constants. However, the following constructs could be useful in special cases. To create a language switch in JavaScript, the selected portal language needs to be identified with the "oHtmlRoot" object.
var l_lang = oHtmlRoot.oUp.oFormatInfo.lang;
switch(l_lang)
{
case "de":
// Code for german language
break;
case "en":
// Code for english language
break;
:
default:
// Fallback if language is missing (default language of the portal)
}
if(l_lang == "de")
{
// Code for german language
}
else if(l_lang == "en")
{
// Code for english language
}
:
else
{
// Fallback if language is missing (default language of the portal)
}
The "oHtmlRoot" object can also be used to identify the defined default language.
var l_defaultLang = oHtmlRoot.oUp.oFormatInfo.defaultLang;
Um im Velocity-Kontext sprachabhängige Weichen zu konstruieren, kann die Intrexx-Systemvariable $lang verwendet werden, die die aktuell eingestellte Portalsprache enthält.
#if($lang == "de")
// Language dependent code
#elseif($lang == "en")
// Language dependent code
#else
// Fallback in case of missing language
#end
Different options are available for generating multilingual data in a Groovy script or to control certain actions based on the language.
// Current portal language
g_language
// Default language of the portal
g_defaultLanguage
// Current portal language via request parameter rq_Lang
g_request.get("rq_Lang")
// Default language Users from the current session
g_session.user.getDefaultLanguage()
A language switch can be created for various purposes using a switch case construction.
switch(g_language)
{
case "de":
return german
break
case "en":
return english
break
default:
return english
}
Multilingual graphics
If graphics are managed via data groups, these can be defined for each language-dependent data record. It is much more difficult to display language-dependent graphics in the layout, as this is not provided for technically. One option for this is to provide the graphic with the ISO code in the filename and then to construct the URL with Velocity using the current portal language. The following ActionControl generated a DIV container with a link to the portal homepage as well as the language-dependent embedding of a graphic. It is important to name the graphic with "logo_<iso-languagecode>.png". The control assembles the filename dynamically by using the current portal language "$lang".
<div id="Container_Logo">
<a title="Home" href="/$Portal.getPortalName()">
<img width="199" height="49" src="images/${layout}/logo_${lang}.png" alt="Home">
</a>
</div>
Velocity variables in language constants
In every language constant with the type "Constant is evaluated as a Velocity expression", Velocity variables can be embedded when these are used on application pages. For this to work correctly, the variable needs to be available in the page context. In the following example, the variable "$Rooms" is written into the text to add a dynamic statement - the number of rooms - to the static text.
Constant text:
There are $Rooms Room/Rooms in this building!
Output:There are 10 room/rooms in this building!
Language switch with flags
A language switch with flags only makes sense for a few portal languages, and only in combination with the language name. For languages such as English, that are represented by multiple countries and therefore flags, a language switch with flags is not always ideal. Intrexx already delivers a set of graphics with flags that possess the ISO code as their name. To begin with, add a new file called "languageswitch_flag.vm" to the portal directory \internal\system\vm\html\actioncontrol and copy the Velocity code below into this file.
#set($l_aAllLang = $WebMenu.getMenuLanguages())
<span id="ID_Languageswitch">#foreach($l_strLang in $l_aAllLang)
#set($l_strImagePath = "images/assets/flags_of_the_world/16x16/plain/${l_strLang}.png")
#set($l_strDisplayLang = $TextUtil.getDisplayLanguage($l_strLang, $l_strLang))
<a style="width: 16px; height: 16px; display: inline-block; background-repeat: no-repeat; background-position: center; background-image: url($l_strImagePath); cursor: pointer;" onclick="var oLangAction=setLangAction('$velocityCount', '$!l_strLang');oLangAction.changeLang();return false;" lang="$!l_strLang" target="_top" href="$Request.get('DEFAULT_URL')?rq_Lang=$!l_strLang" id="ID_actionLangSwitch${velocityCount}" title="$I18N.get('LANGUAGESWITCH_DESCRIPTION')"></a>#end
</span>
<script type="text/javascript">
function setLangAction(count, lang){oLangAction = new upTextActionControl();oLangAction = oLangAction.biDirectUpHtml(oLangAction, 'ID_actionLangSwitch' + count);oLangAction.linkType = '4';oLangAction.oTarget = new upTarget();oLangAction.oTarget.rq_Lang = lang;return oLangAction;}
</script>
In the file "controls.xml", add the following block to the XML structure:
<control id="Action_LanguageSwitchFlag" mobile="false" multipleUse="false" vm="languageswitch_flag.vm">
<title lang="en" value="Language Switch with Flags"/>
<title lang="de" value="Sprachumschalter mit Flaggen"/>
<description lang="en" value="Language Switch"/>
<description lang="de" value="Sprachumschalter"/>
</control>
After restarting the Portal Manager, the additional control can be selected accordingly and added to the layout.