Groovy handler in applications
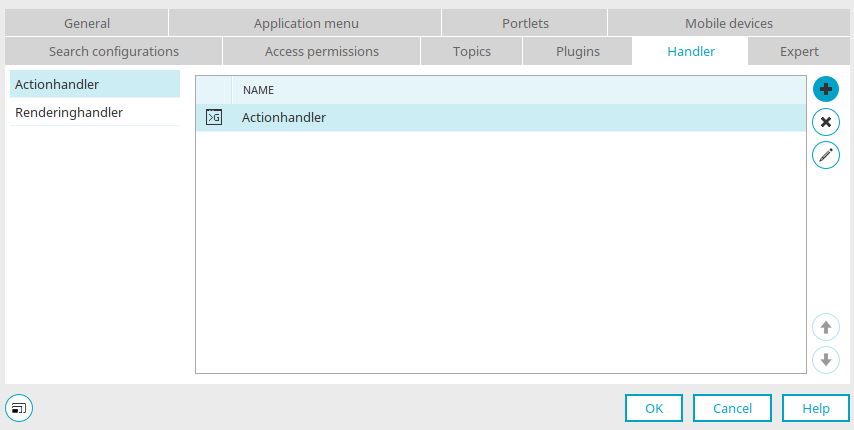
"Handler" tab
If the expert options are activated, you can access this dialog in the properties dialog of an application and in the properties dialog of its pages and data groups. Handlers can be defined here that can be used to execute Groovy scripts.
ActionHandler
Reacts to actions such as saving and deleting.
RenderingHandlers
Is activated when the page is rendered.
Examples for the use of handlers
Action handlers can be used, for example, to write values from a data record when a new record is saved in a processing context, such as to create a history of a process. An additional example of an application would be to generate IDs, such as "NAME_YEAR_CUMULATIVE_NUMBER" from various edit fields. If this problem is solved with a handler, neither a specific process nor JavaScript is required. For security reasons, the use of a handler is advantageous as well, since code is run on the server instead of client-side.
Script execution
The scripts are run in the corresponding environment where they are saved – Scripts on a page are only run for that page, while scripts in data groups are run on all pages and actions contained in the data group, and Scripts in the application node are run application-wide.
![]() Remove handler definition
Remove handler definition
The currently handler definition is deleted.
![]()
![]() Move up / Move down
Move up / Move down
Adjust the order of the handlers.
![]() Add handler definition /
Add handler definition / ![]() Edit handler definition
Edit handler definition
Opens a dialog in which a new handler can be defined or an existing handler definition can be edited.
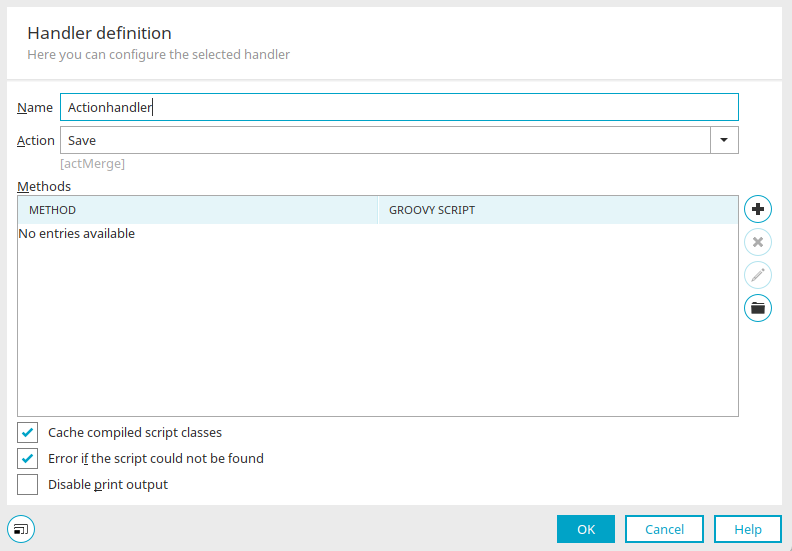
Handler definition
Name
Enter a name for the new handler here.
Action
If you are defining an action handler, select the desired action underneath that will be used to trigger the script. This option is not available for rendering handlers.
"Method" column
The method is stated here.
"Groovy script" column
States the path to the referenced Groovy script file.
![]() Add method
Add method
Select the desired time at which the script is run here. You can select from the following phases here:
-
processBefore
Script is run before the request is processed.
-
processBeforeWorkflow
Only for action handlers. Executes after a request, before a process is run.
-
processAfter
Executes at the end of a process.
Once the desired method is selected, the Groovy file manager will open automatically, where the storage location of the script can be defined.
The storage location is in the portal directory "internal/application/store/<application-GUID>/groovy".
You can find this out by selecting the application node and then pressing F4. This will only work if the expert options have been activated. There is also an order for processing within the two handler types according to the application structure:
RenderingHandlers
processBefore:
-
RenderingHandler of the application
-
RenderingHandler of the data group
-
RenderingHandler of the page
processAfter: The reverse order of above
ActionHandler
processBefore and processBeforeWorkflow:
-
ActionHandler of the application
-
ActionHandler of the data group
-
ActionHandler of the page
processAfter: The reverse order of above
![]() Remove method
Remove method
Removes the method currently selected in the list.
![]() Edit script
Edit script
Opens the script editor.
![]() Select script file
Select script file
Opens the Groovy file manager.
Cache compiled script classes
The compiled Groovy script classes are stored in the cache.
Error when the script does not exist
Displays a message when the referenced script is not found.
Disable print output
Disables PrintIn messages.